In this tutorial, we'll explore a straightforward Python program that leverages the power of the os module and a graphical user interface library called PyQt6 to create a basic File List App. This application allows users to open a folder and view the list of files within it.
The Python Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 | import sys from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QFileDialog, QListWidget, QPushButton, QWidget import os class FileListApp(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('File List App') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300) # Create widgets self.list_widget = QListWidget(self) self.open_button = QPushButton('Open Folder', self) self.open_button.clicked.connect(self.openFolder) # Create layout layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.open_button) layout.addWidget(self.list_widget) # Create central widget and set layout central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def openFolder(self): folder_path = QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory(self, 'Open Folder') if folder_path: self.displayFiles(folder_path) def displayFiles(self, folder_path): # Clear the current list self.list_widget.clear() # Get the list of files in the folder file_list = [f for f in os.listdir(folder_path) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(folder_path, f))] # Add files to the QListWidget self.list_widget.addItems(file_list) def main(): app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = FileListApp() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec()) if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
The Output
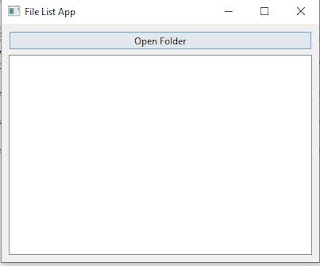
a) The Initial Screen: (click the "Open Folder" button to go to next screen)
b) The Open Folder Dialog Box: (select a folder)
c) The Result(the listbox on the first screen contains the files onside the selected folder)
Understanding the Code
- Class FileListApp: Represents the main application window and inherits from QMainWindow.
- Method initUI: Initializes the user interface by setting the window title, dimensions, creating widgets (QListWidget and QPushButton), and defining the layout.
- Method openFolder: Utilizes QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory to prompt the user to select a folder. If a folder is selected, it calls the displayFiles method.
- Method displayFiles: Clears the existing file list in the QListWidget, retrieves the list of files in the selected folder, and adds them to the QListWidget.
- Method main: The main entry point of the application. It creates an instance of FileListApp and starts the application loop.
- The graphical interface enhances user interaction by providing a familiar and intuitive way to select folders.
- The program dynamically lists files within the chosen folder, showcasing the flexibility of Python in managing file-related operations.
- Python's cross-platform compatibility ensures that this code can run seamlessly on various operating systems without modification.
- The code structure follows best practices, making it readable and maintainable. It serves as a foundation for expanding functionality or integrating into larger applications.
- Python's extensive community support ensures that developers can find resources and assistance easily, making it an ideal choice for diverse applications.